Center for Clinical Epidemiology & Population Health
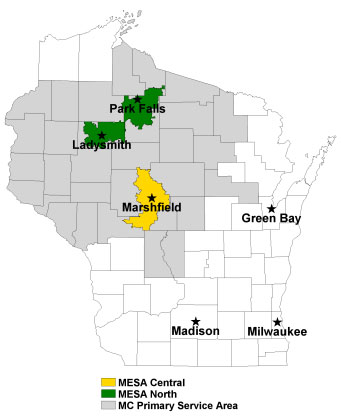 The Marshfield Epidemiologic Study Area (MESA) is a geographic region defined by zip codes where the great majority of residents choose to receive medical care at Marshfield Clinic Health System, its regional centers and affiliated hospitals. It is a unique resource for population-based health research when combined with health data from the Health System.
The Marshfield Epidemiologic Study Area (MESA) is a geographic region defined by zip codes where the great majority of residents choose to receive medical care at Marshfield Clinic Health System, its regional centers and affiliated hospitals. It is a unique resource for population-based health research when combined with health data from the Health System.
Automated daily review of Health System computerized databases finds and follows all residents within a 24-ZIP code region in northern and central Wisconsin served by the Health System. Since MESA was launched by Marshfield Epidemiology Research Center staff in July 1991 (DeStefano 1996), the resulting dynamic cohort has grown to include individual follow-up time on more than 185,000 people.
MESA has residents living in the city of Marshfield and the rest living in rural areas – small towns, villages and countryside. MESA is divided into two main regions. The largest region, called MESA Central, includes people in 14 ZIP code areas clustered around Marshfield Marshfield Medical Center in Marshfield. The remaining MESA residents live in a region called MESA North, which includes 10 ZIP code areas near Park Falls, Phillips and Ladysmith.
Unique Features of MESA
Because the Health System databases capture nearly all residents of the MESA region, research using MESA represents an entire population, not only specific subpopulations typically studied by major HMOs and insurance companies. In addition, through provision of primary, secondary and tertiary care, the full clinical spectrum of disease is represented, not only the more severe cases often studied at hospital- or referral-based research centers. Unlike most other research facilities, MESA researchers can monitor the residency of individuals on a daily basis by using updates of births, deaths, new patients, and name and address changes to Health System databases. This allows researchers to track the health of a community over time by linking this residency information with the extensive inpatient and outpatient health care information available in Health System databases and medical records. (Greenlee 2003)
MESA's unique features include:
- Stability of the population: The available records include many families dating back several generations. The mobility of the population is lower than for many other areas, making this an ideal population in which to study long-term conditions and inherited diseases.
- Available data: Medical information for MESA residents is comprehensive, in large part because our clinic and hospitals in the Marshfield area have shared a common medical record for patients since the early 1900s. Diagnostic codes for each patient have been computerized since 1960 and medical procedure codes have been archived since 1985. Individual patient records have been kept in an extensive electronic medical system since the early 1990s.
- Participation in research: MESA residents have recognized the importance of medical research. This has resulted in participation rates over 60 percent, and as high as 90 percent, in surveys and long-term studies.
MESA and Research
Through collaborations with Health System clinician researchers, other Marshfield Clinic Research Institute scientists and external partners, including the CDC, MESA has been a productive resource for population-based research. Since 1994, this work has resulted in more than 70 peer-reviewed scientific publications and numerous presentations across a wide variety of epidemiologic and clinical topics. Over the years, the unique capacity of the MESA resource has also played a key role in externally-funded research grants.
Validation of MESA Data
MESA data is periodically validated. The most recent validation indicated that Health System databases captured 97% of residents, 95% of hospital discharges, 93% of medical outpatient visits and 98% of deaths among MESA Central residents. Health System databases captured 92% of people, 87% of hospital discharges, 91% of outpatient visits and 95% of deaths for MESA North.
MESA Farm Resident Cohort
Agricultural activity plays a large role in MESA, both economically and culturally. In order to study the unique characteristics of farm-related injuries and conditions, a cohort of farm residents within MESA was created using a variety of sources. All potential MESA database farm residents were contacted to validate the farm residency of themselves and their family members. The most recent farm resident cohort, created in 1998, revealed 5,432 farm residents in MESA.
Key References:
1. DeStefano F, Eaker ED, Broste SK, Nordstrom DL, Peissig PL, Vierkant RA, Konitzer KA, Gruber RL, Layde PM. Epidemiologic Research in an Integrated Regional Medical Care System: The Marshfield Epidemiologic Study Area. J Clin Epidemiol 1996;49:643-652.
2. Greenlee RT. Measuring Disease Frequency in The Marshfield Epidemiologic Study Area (MESA). Clinical Medicine and Research 2003; 1(4):273-280.
